Research shows that more than 90 percent of all systemic diseases have oral manifestations. Your dentist is likely the first diagnosis, long before your physician. Some of these diseases include:
Diabetes, Leukemia, diabetes, osteoporosis, stroke, Pancreatic cancer, Heart disease, Kidney disease, Alzheimers disease and more.
-

Mouth Cancer
More than 90 percent of mouth cancers are squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that look like fish scales. They are found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Carcinoma means cancer.
Squamous cell carcinoma most commonly appears on parts of the body frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, and neck. But it also arises in the mouth.
Less common cancers of the oral cavity include Oral Verrucous Carcinoma and Oral Melanoma
-
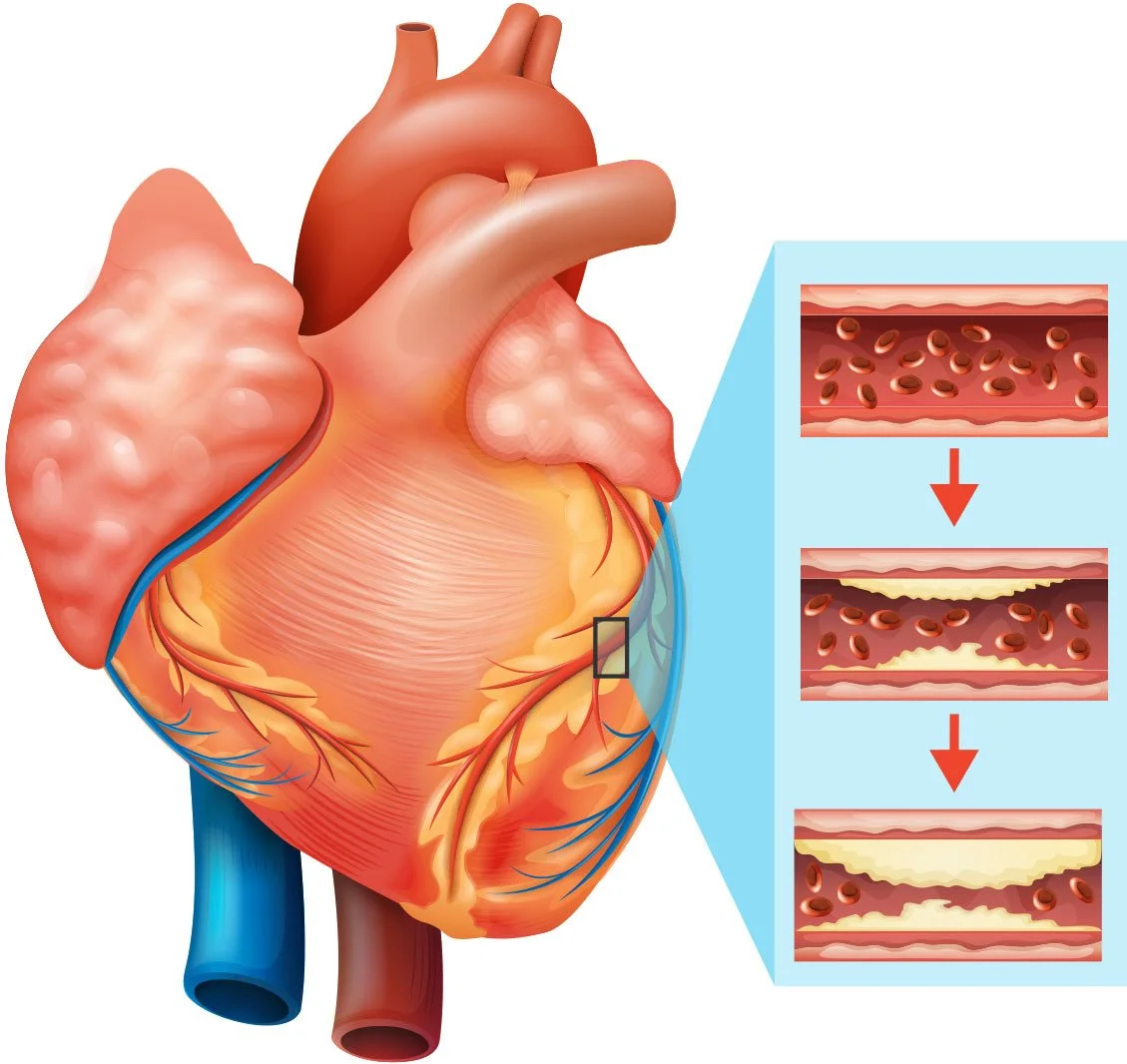
Heart Disease
Research shows gum disease is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease: the more severe the periodontitis, the higher the risk.”
Bacteria spread through your bloodstream from the mouth to other bodily areas. These microorganisms are the link between gum disease and specific heart conditions, such as endocarditis, atherosclerosis (clogged arteries), and stroke, but could potentially also pose a risk to other heart conditions.
-

Stroke
Description goes here -

Meth Mouth/ Drug Use
Methamphetamine (meth) is a dangerously addictive drug that can have severe health consequences, including stroke and permanent brain damage. “Meth mouth” is characterized by severe tooth decay and gum disease, which often causes teeth to break or fall out.
The teeth of people addicted to methamphetamines are characterized by being blackened, stained, rotting, crumbling and falling apart. Often, the teeth cannot be salvaged and must be removed. The extensive tooth decay is likely caused by a combination of drug-induced psychological and physiological changes resulting in dry mouth and long periods of poor oral hygiene. Methamphetamine itself is also acidic.
The study found that the more meth a person used, the worse their tooth decay was. While high, users often crave high-calorie, carbonated, sugary beverages. In addition, they may grind or clench their teeth, all of which can harm teeth.
-
Respiratory Disease
Description goes here -

Pregnancy
Description goes here -

Rotten Teeth (child)
Description goes here -

Periodontal Disease/ Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease, also called periodontal disease. It causes irritation, redness, swelling and bleeding of your gingiva, which is the part of your gum around the base of your teeth. It's important to take gingivitis seriously and treat it promptly.
-
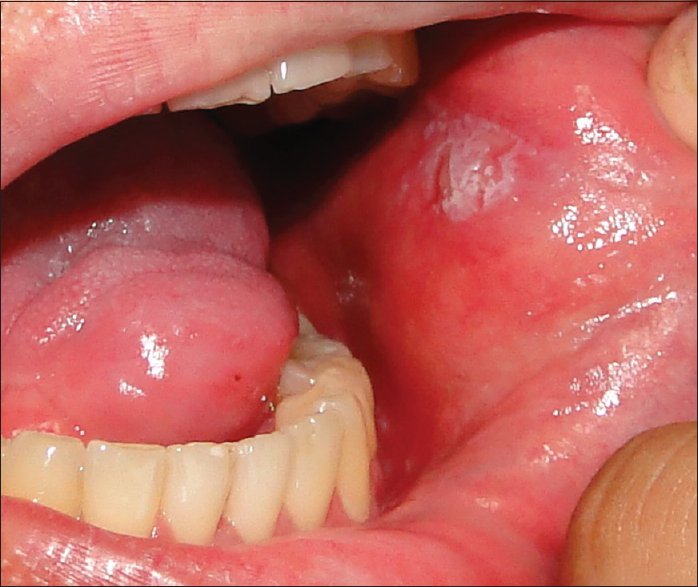
Buccal Mucosa Cancer
Inner cheek cancer (also called buccal mucosa cancer) is a type of head and neck cancer that begins when the cells that make up the inner cheek grow out of control and form lesions or tumors. Buccal mucosa is another name for the inside lining of the cheeks.
-
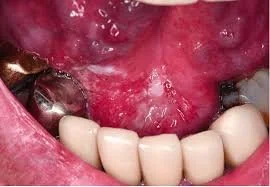
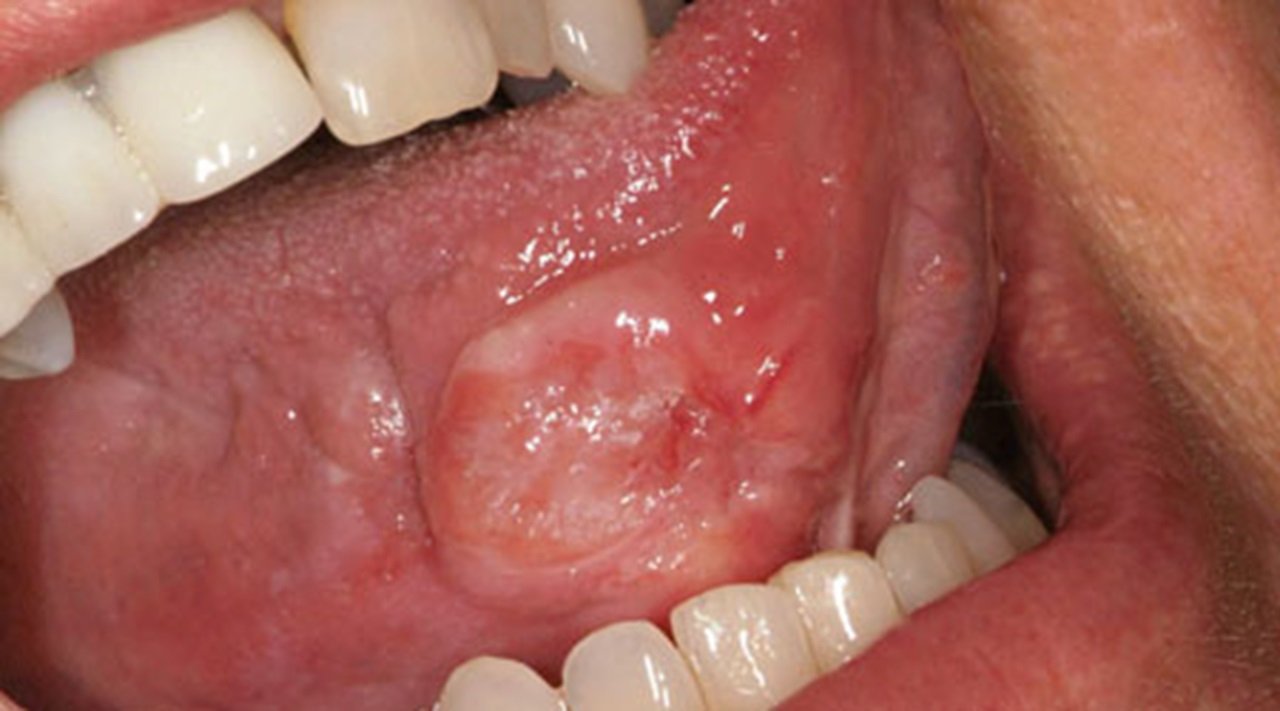
Floor of the Mouth Cancer
Floor of mouth cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that begins when the cells that make up the floor of the mouth (the horseshoe-shaped area under the tongue) grow out of control and form lesions or tumors. These cancers are often mistaken for canker sores.
Using tobacco products, particularly chewing tobacco, and regularly drinking too much alcohol can increase your chances of developing cancer in the floor of your mouth. Dentists are typically the first to notice signs of floor of mouth cancer, often during a routine exam.
The most common symptom of floor of mouth cancer is a sore in your mouth that keeps growing larger. Other signs of cancer in the floor of the mouth include white, red, or dark patches in the mouth, mouth pain, or a lump in your neck
-

Gum Cancer (Mouth Cancer)
Gum cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that begins when cells in the upper or lower gums grow out of control and form lesions or tumors. These cancers are often mistaken for gingivitis.
Gum cancer most often affects people over age 60. Signs of gum cancer include sores, white patches, bleeding and pain or numbness on the gums. The symptoms can mimic those of gingivitis or a gum or tooth infection. Gum cancer can spread to structures such as the sinuses or jawbone.
Symptoms of gum cancer may include:
white, red, or dark patches on the gums, bleeding or cracking gums or thick areas of the gums
-

Hard Palate Cancer
Hard palate cancer is a type of head and neck cancer that begins when cells that make up the bony part of the roof of the mouth grow out of control and form lesions or tumors.
The hard palate creates a barrier between the mouth and the nasal cavity. Cancers that develop there tend to spread into the nasal cavity when they become more advanced.
The most common sign of hard palate cancer is an ulcer on the roof of the mouth. As the cancer grows, the ulcer may bleed.
Other symptoms of hard palate cancer include the following:
bad breath
loose teeth or pain around your teeth
dentures that no longer fit
changes in speech
difficulty swallowing
difficulty moving your jaw
a lump in the neck
-
Tongue Cancer
There are two parts to your tongue, the oral tongue and the base of the tongue. Cancer can develop in either part. The oral tongue is the part you see when you stick out your tongue. This is the front two-thirds of your tongue.
The base of the tongue is the back third of the tongue. This part is very near your throat (pharynx). Cancer that develops in this part is classified as oropharynx cancer, or throat cancer.
Cancer of the tongue can affect anyone. Most cases are linked to tobacco use and heavy alcohol consumption. Other risk factors for tongue cancer include being male and being over age 40,
Many tongue cancers are first discovered during routine dental exams, so it’s important to see your dentist regularly, especially if you’re at an increased risk for tongue cancer.
Tongue Cancer Symptoms
The symptoms of tongue cancer may include the following:
Red, white, or dark patches on the tongue
a sore throat that does not go away
a sore spot (ulcer) or lump on the tongue that does not go away
pain when swallowing
mouth numbness
bleeding from the tongue
